Recumbent length can also used for children two to three years of age who have great difficulty standing on their own. These children must be measured lying down and the measurement should be recorded as recumbent length.
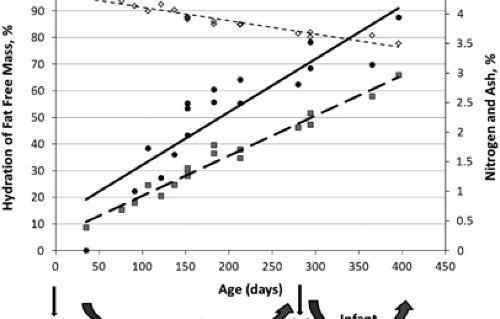
Higher Fat Mass And Fat Mass Accretion During The First Six
Measurement of body composition in infants. The pea pod is extremely simple to operate with software prompts guiding the operator through each step of the process. The body composition of children from birth to 16 years of age has been measured using this method table 1 1 3. However there remains a gap for use in children from 6 months to about 5 years of age. Quantitative magnetic resonance qmr has been increasingly used to measure human body composition but its use and validation in children is limited. The pea pod is an air displacement plethysmography adp system using whole body densitometry to determine body composition fat and fat free mass in infants weighing between 1 and 8 kg. Adp is now considered a criterion method of body composition analysis in children 18 and in several studies it has provided more accurate measurements of body fat than dxa 19 20.
Measurements are taken from 4 sites. Currently the pea pod is the only commercially available technology that allows for accurate body composition assessment of newborns. The accuracy as a tool for assessing body composition has been compared against dual energy x ray absorptiometry dxa in term infants at birth and 2 and 4 months of age showing a high degree of agreement and correlation. Dual energy x ray absorptiometry dxa 3 is used increasingly as the method of choice to measure various components of body composition bc during infancy koo 2000. Dual energy x ray absorptiometry dxa is a method to assess body composition based on the three compartment model. Two instruments are commercially available for adp assessment of body composition.
The peapod figure 14 has been shown to be accurate in comparison to underwater weighing for assessment of. Hence accurate and non invasive measurement of infant body composition which evaluates the quality in addition to the amount of weight gain represents a useful tool for gaining further insight into the relationship between birth weight or time in utero and future development. The adp has been validated for use in infants from birth to 8 kg 6 months and in children older than 5 years. Recumbent length is used to measure infants and children less than two years of age. We reported previously that body mass is the dominant predictor of bone mineral status in newborns koo et al. 1996 and older infants koo et al.